Skip to content
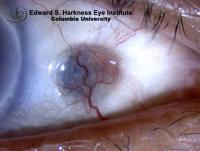
Scleral Thinning
- Topical antimetabolites such as mitomycin-C or triethylene thiophosphamide have been routinely used as an adjunctive therapy after pterygium removal surgery to decrease the likelihood of recurrency.
- May be complicated with corneal or scleral thinning, ulceration and necrosis especially when bare scleral technique is applied.
Clinical Features
- Symptoms: may be asymptomatic or associated with ocular irritation
- Signs:
- Scleral thinning with trans-sclerally visible choroid
- Hyperemia of the overlying conjunctiva
- May progress to scleral perforation
Management
- Observation, if asymptomatic and no evidence of perforation.
- Surgical patch grafts to reinforce the thinning sclera.
Back to top