Skip to content
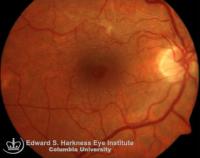
Pseudohole
- Retinal lesion that simulates macular hole without actual tissue loss.
Clinical Features
- Altered light reflex and darker appearance of the fovea
- Steepening of the normal foveal depression
- Most commonly seen in association with epiretinal membrane contraction, vitreomacular traction syndromes, proliferative diabetic retinopathy, rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, intraocular inflammation, trauma and venous occlusive disease
- Optical coherent tomography (OCT) demonstrates:
- Steepening of foveal contour
- Full thickness retinal tissue is present
- Reflective epiretinal membrane layer is present on the surface of the retina
- Fluorescein angiography often reveals normal fluorescence except if traction-induced retinal vascular disruption present.
Management
- Treatment of the underlying causes of epiretinal membrane.
- Observation of progressive contraction, which may lead to macular edema.
- Surgical vitrectomy to peel the epiretinal membrane may be indicated in patients with worsening vision of 20/80 or less.
Back to top